Werbung
Quicklinks
Gebrauchsanweisung
MACS
Instructions for use
MACS
Mode d'emploi
Vis polyaxiale MACS
Instrucciones de manejo
Tornillo poliaxial MACS
Istruzioni per l'uso
Vite poliassiale MACS
Instruções de utilização
Parafuso poliaxial MACS
Gebruiksaanwijzing
MACS
AESCULAP AG & CO. KG
Am Aesculap-Platz
78532 Tuttlingen/Germany
Phone +49 (74 61) 95-0
Fax
+49 (74 61) 95-26 00
E-mail information@aesculap.de
TL
-Polyaxialschraube XL
TL
polyaxial screw XL
TL
-polyaxiale schroef XL
TL
XL
TL
XL
TL
XL
TL
XL
Werbung

Inhaltszusammenfassung für B. Braun AESCULAP MACSTL XL
- Seite 1 Gebrauchsanweisung MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL Instructions for use MACS polyaxial screw XL Mode d’emploi Vis polyaxiale MACS Instrucciones de manejo Tornillo poliaxial MACS Istruzioni per l’uso Vite poliassiale MACS Instruções de utilização Parafuso poliaxial MACS Gebruiksaanwijzing MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL AESCULAP AG & CO. KG Am Aesculap-Platz 78532 Tuttlingen/Germany Phone +49 (74 61) 95-0...
- Seite 3 MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL Verwendungszweck Die MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL dient in Kombination mit den anderen MACS -Implantaten des MACS -Systems der ventralen mono- und multisegmentalen Stabilisierung der lumbalen und thorakalen Wirbelsäule. Das MACS -System besteht aus: • Verankerungsschrauben für die Wirbelkörper •...
- Seite 4 MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL Indikationen Operativ eingesetzte Implantate dienen der Unterstützung nor- maler Heilungsprozesse. Sie sollen weder normale Körperstruktu- ren ersetzen noch im Falle nicht vollzogener Heilung die auftre- tenden Belastungen dauerhaft übernehmen. Verwenden bei: • Frakturen • Spinalem Tumor • Degenerativem Bandscheibenschaden (Spondylolisthesis, Spondylolyse, spinale Stenose) •...
- Seite 5 MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL • Schwerer Osteopenie Bei Osteopenie muss der Operateur die Risiken abwägen, die den Therapieerfolg des MACS -Systems gefährden könnten. Bei zu erwartendem, verringertem Halt der Standard-Poly- axialschraube kann die Polyaxialschraube XL verwendet wer- den. Bei Bedarf kann die Polyaxialschraube XL zur weiteren Erhöhung der Verankerungsstabilität mit einem für die Schraubenaugmentation geeigneten Aesculap-Zement fixiert werden.
- Seite 6 MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL Neben- und Wechselwirkungen • Implantatversagen durch Überbelastung – Biegung – Lockerung – Bruch • Mangelnde Fixierung • Keine oder verspätete Fusion • Zementleckagen (Zementaustritt aus dem Wirbelkörper) • Infektion • Wirbelkörperfraktur • Verletzungen von – Nervenwurzeln – Rückenmark –...
- Seite 7 MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL • Der Operateur muss mit der Knochenanatomie, dem Verlauf der Nerven und Blutgefäße, der Muskeln und Sehnen absolut vertraut sein. • Der Operateur ist für die Zusammenstellung der Implantat- komponenten und deren Implantation verantwortlich. • Aesculap ist nicht verantwortlich für Komplikationen durch falsche Indikationsstellung, Implantatauswahl, falsche Kom- bination von Implantatkomponenten und Operationstechnik sowie Grenzen der Behandlungsmethode oder fehlende...
- Seite 8 MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL • Bei Schädigung der kraftübertragenden Knochenstrukturen sind Lockerungen der Komponenten, Knochen- oder Implan- tatfrakturen und andere schwerwiegende Komplikationen nicht auszuschließen. Um derartige Fehlerquellen möglichst frühzeitig zu erkennen, muss der Zustand der Implantatversorgung nach der Opera- tion periodisch durch geeignete Maßnahmen überprüft wer- den.
- Seite 9 MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL Sterilität • Die Implantatkomponenten werden unsteril geliefert. • Die Implantatkomponenten sind einzeln verpackt. Implantatkomponenten in der Originalverpackung lagern und erst unmittelbar vor dem Einsatz aus der Original- und Schutzverpackung nehmen. Vor dem Einsatz Implantate vorreinigen und dampf- sterilisieren (nach den im Krankenhaus geltenden Richtlinien zur Herstellung von Sterilgut).
- Seite 10 MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL Anwendung Das MACS -System ist im OP-Manual ausführlich beschrieben. Detaillierte Anwendungshinweise sind den Produktunterlagen zu entnehmen. Das OP-Manual kann jederzeit beim Hersteller angefordert wer- den. Der Operateur erstellt eine Operationsplanung, die Folgendes festlegt und geeignet dokumentiert: • Auswahl und Dimensionierung der Implantatkomponenten •...
- Seite 11 MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL • Operateur und Operationsteam kennen Informationen zur Operationstechnik, zum Implantatsortiment und zum Instru- mentarium; die Informationen sind vor Ort vollständig vor- handen • Regeln der ärztlichen Kunst, Stand der Wissenschaft und In- halte einschlägiger wissenschaftlicher Veröffentlichungen der medizinischen Autoren bekannt •...
- Seite 12 MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL Die Implantation des MACS -Systems erfordert folgende An- wendungsschritte: Geeignete MACS -Systemvariante und Verankerungs- schrauben auf Basis der Indikation, der präoperativen Pla- nung und der intraoperativ vorgefundenen knöchernen Situ- ation wählen. Optimale Implantatposition des MACS -Systems ermitteln: –...
- Seite 13 MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL Einsetzinstrument entfernen. Sicherstellen, dass die Zentrierhülsen auf den Spannelemen- ten temporär montiert bleiben. Evtl. distrahieren und Platzhalter einsetzen. Verletzungsgefahr durch Auslockern oder Ausreißen der Schrauben während des Re- ponierens, Distrahierens bzw. Komprimie- rens, insbesondere in Fällen schlechter WARNUNG Knochenqualität! Kraft vorsichtig und dosiert einleiten.
- Seite 14 MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL Bei Bedarf Polyaxialschraube XL mit einem für die Schrau- benaugmentation geeigneten Aesculap-Zement zementie- ren. Sicherheitshinweise des Aesculap-Zementapplikationssys- tems unbedingt beachten. Verletzungsgefahr durch Zementleckagen! Implantate nur mit Hilfe von bildgeben- den Verfahren präparieren und positio- nieren. WARNUNG Darauf achten, dass die Schlitze der Po- lyaxialschraube XL vollständig im Kno- chen liegen.
- Seite 15 MACS -Polyaxialschraube XL Klemmschraube einsetzen. Verletzungsgefahr durch nicht einsetzbare bzw. anziehbare Klemmschrauben aufgrund des aushärtenden Zements! Klemmschrauben unmittelbar nach dem WARNUNG Zementieren der Polyaxialschraube XL aufsetzen und anziehen. Verletzungsgefahr durch unzureichend an- gezogene Klemmschrauben der Polyaxialele- mente! Klemmschrauben korrekt aufsetzen. WARNUNG Klemmschrauben mit einem Drehmo- mentschlüssel mit 10 Nm anziehen.
- Seite 16 MACS polyaxial screw XL – Not applicable for the USA – See version for the USA – Intended use The MACS polyaxial screw XL, in combination with the other MACS implants of the MACS system, is used for the ventral mono- and multisegmental stabilization of the lumbar and tho- racic spine.
- Seite 17 MACS polyaxial screw XL – Not applicable for the USA – See version for the USA – Indications Surgically installed implants serve to support normal healing pro- cesses. They are not supposed to replace normal body structures or to support permanently loads occurring in cases where healing did not take place.
- Seite 18 MACS polyaxial screw XL – Not applicable for the USA – See version for the USA – • Acute osteopenia In cases of osteopenia, the operating surgeon has to weigh the risks that may endanger the success of a therapy with the MACS system.
- Seite 19 MACS polyaxial screw XL – Not applicable for the USA – See version for the USA – Side-effects or adverse interactions • Implant failure resulting from excess load – bending – loosening – breakage • Inadequate fixation • Absence of, or delayed, bony union •...
- Seite 20 MACS polyaxial screw XL – Not applicable for the USA – See version for the USA – Safety information This system is not licensed to be screwed onto, or fastened to, the posterior elements (pedicles) of the cervical, thoracic or lumbar spine.
- Seite 21 MACS polyaxial screw XL – Not applicable for the USA – See version for the USA – • Under no circumstances may damaged components or surgi- cally excised components be used. • Implants once used must not be reused. • The implant components applied, along with their article numbers, the name of the implant, as well as the batch num- ber and serial number (if available) must be documented in...
- Seite 22 MACS polyaxial screw XL – Not applicable for the USA – See version for the USA – Sterility • The implant components are delivered unsterile. • The implant components are delivered in individual packag- ing. Store the implant components in their original packaging and only remove them from such packaging immediately be- fore use.
- Seite 23 MACS polyaxial screw XL – Not applicable for the USA – See version for the USA – Application The MACS system is described in detail in the O.R. manual. De- tailed user instructions can be found in the product documenta- tion.
- Seite 24 MACS polyaxial screw XL – Not applicable for the USA – See version for the USA – • The operating surgeon and operating room team must be thoroughly conversant with the operating technique, as well as the range of implants and instruments to be applied; com- plete information on these subjects must be readily available at the workplace •...
- Seite 25 MACS polyaxial screw XL – Not applicable for the USA – See version for the USA – The implantation of the MACS system has to be carried out in the following steps: Select the appropriate MACS system variant and anchoring screws according to indication, preoperative planning and bone situation found intraoperatively.
- Seite 26 MACS polyaxial screw XL – Not applicable for the USA – See version for the USA – Remove the insertion instrument. Ensure that the centering sleeves remain mounted, tempo- rarily, on the clamping elements. Distract and insert placeholder, if necessary. Risk of injury caused by screws loosening or tearing out during reposition, distraction or compression, especially in cases of poor...
- Seite 27 MACS polyaxial screw XL – Not applicable for the USA – See version for the USA – If necessary, cement the polyaxial screw XL with an Aesculap cement suitable for screw augmentation. Always follow the safety advice for the Aesculap cement ap- plication system.
- Seite 28 MACS polyaxial screw XL – Not applicable for the USA – See version for the USA – Insert clamping screw. Risk of injury caused by clamping screws that cannot be inserted or tightened be- cause the cement is already hardening! Put in place and tighten the clamping WARNING screws immediately after cementing the...
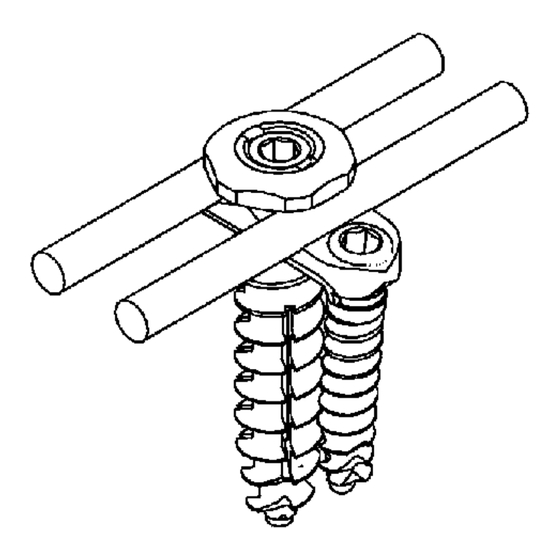
- Seite 29 MACS polyaxial screw XL CAUTION Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on order of a physician! Intended use This anterolateral/anterior system consists of several vertebral screws, locking nuts, spine plates and rods. The points of attachment are screw fixation to the anterolateral vertebral bodies of the lumbar and thoracic spine (T1 to L5).
- Seite 30 MACS polyaxial screw XL Materials The materials used in the implant are listed on the package. • ISOTAN® titanium forged alloy Ti6Al4V according to ISO 5832-3 MACS ® and ISOTAN® are registered trademarks of AESCULAP AG & CO. KG, 78532 Tuttlingen/Germany. System configurations •...
- Seite 31 MACS polyaxial screw XL Contraindications Do not apply in the presence of: • Infection – systemic – in the spine – local • Pregnancy • Acute osteopenia In cases of osteopenia, the operating surgeon has to weigh the risks that may endanger the success of a therapy with the MACS system.
- Seite 32 MACS polyaxial screw XL Side-effects or adverse interactions • Implant failure resulting from excess load – bending – loosening – breakage • Inadequate fixation • Absence of, or delayed, bony union • Infection • Fractured vertebral body or bodies • Injuries to –...
- Seite 33 MACS polyaxial screw XL Safety information This system is not licensed to be screwed onto, or fastened to, the posterior elements (pedicles) of the cervical, thoracic or lumbar spine. • It is the operating surgeon’s responsibility to ensure that im- plant components are applied correctly during operative pro- cedures.
- Seite 34 MACS polyaxial screw XL • Under no circumstances may damaged components or surgi- cally excised components be used. • Implants once used must not be reused. • The implant components applied, along with their article numbers, the name of the implant, as well as the batch num- ber and serial number (if available) must be documented in all patient records.
- Seite 35 MACS polyaxial screw XL Sterility • The implant components are delivered unsterile. • The implant components are delivered in individual packag- ing. Store the implant components in their original packaging and only remove them from such packaging immediately be- fore use. Pre-clean and steam-sterilize the implants (according to the respective hospital guidelines for the provision of sterile ma- terials) before use.
- Seite 36 MACS polyaxial screw XL Sterilization for the US market: • Sterilization of the device may be accomplished by steam. • Aesculap does not recommend the device be sterilized by “Flash” or chemical sterilization. • Surgical instruments may also be placed within an Aesculap rigid sterilization container (sterile container) for processing under generally accepted hospital in-use conditions.
- Seite 37 MACS polyaxial screw XL Application The MACS system is described in detail in the O.R. manual. De- tailed user instructions can be found in the product documenta- tion. The O.R. manual can be ordered from the manufacturer at any time. The operating surgeon shall devise an operation plan that speci- fies and accurately documents the following: •...
- Seite 38 MACS polyaxial screw XL • The operating surgeon and operating room team must be thoroughly conversant with the operating technique, as well as the range of implants and instruments to be applied; com- plete information on these subjects must be readily available at the workplace •...
- Seite 39 MACS polyaxial screw XL The implantation of the MACS system has to be carried out in the following steps: Select the appropriate MACS system variant and anchoring screws according to indication, preoperative planning and bone situation found intraoperatively. To determine the optimum implant position of the MACS system: –...
- Seite 40 MACS polyaxial screw XL Remove the insertion instrument. Ensure that the centering sleeves remain mounted, tempo- rarily, on the clamping elements. Distract and insert placeholder, if necessary. Risk of injury caused by screws loosening or tearing out during reposition, distraction or compression, especially in cases of poor bone quality! WARNING...
- Seite 41 MACS polyaxial screw XL Risk of injury caused by insufficiently tight- ened clamping screws of the polyaxial ele- ments! Set clamping screws in place correctly. WARNING Use a torque wrench to tighten the clamping screws at 10 Nm. Further information on Aesculap implant systems is available from Aesculap or the Aesculap office responsible.
- Seite 42 Vis polyaxiale MACS Champ d’application La vis polyaxiale MACS XL, en combinaison avec les autres im- plants MACS du système MACS , sert à la stabilisation ventrale mono- et multisegmentaire de la colonne vertébrale lombaire et thoracique. Le système MACS est composé: •...
- Seite 43 Vis polyaxiale MACS Indications Les implants mis en place par opération ont pour but de contri- buer aux processus normaux de guérison. Ils n’ont pas pour but de remplacer des structures corporelles normales ni de prendre durablement en charge des contraintes en cas de guérison non encore achevée.
- Seite 44 Vis polyaxiale MACS • Ostéopénie grave En cas d’ostéopénie, le chirurgien doit soupeser les risques pouvant remettre en cause la réussite thérapeutique du sys- tème MACS Si l’on s’attend à une tenue réduite de la vis polyaxiale stan- dard, on peut utiliser la vis polyaxiale XL. Si nécessaire et pour obtenir une hausse de la stabilité...
- Seite 45 Vis polyaxiale MACS Effets secondaires et interactions • Défaillance de l’implant due à une contrainte excessive – Fléchissement – Relâchement – Rupture • Fixation insuffisante • Fusion nulle ou retardée • Fuites de ciment (sortie de ciment hors du corps vertébral) •...
- Seite 46 Vis polyaxiale MACS • Le chirurgien est parfaitement familiarisé avec l’anatomie osseuse, le tracé des nerfs et des vaisseaux sanguins, des muscles et des tendons. • Le chirurgien est responsable de l’assortiment des compo- sants d’implant et de leur implantation. •...
- Seite 47 Vis polyaxiale MACS • En cas de détérioration des structures osseuses qui transmet- tent les forces, un relâchement des composants, des fractu- res de l’os ou de l’implant et autres complications graves ne peuvent être exclus. Pour identifier à un stade aussi précoce que possible de telles sources d’erreurs, l’état du traitement par implant doit être contrôlé...
- Seite 48 Vis polyaxiale MACS Stérilité • Les composants d’implants sont livrés non stériles. • Les composants d’implant sont emballés individuellement. Stockez les composants d’implant dans leur emballage d’ori- gine et ne les retirez de l’emballage protecteur d’origine qu’immédiatement avant leur utilisation. Avant l’utilisation, néttoyez les implants préalablement et stériliséz-les à...
- Seite 49 Vis polyaxiale MACS Application Le système MACS est décrit en détail dans le Manuel opératoire. Les documents accompagnant le produit doivent être consultés pour des conseils d’application détaillés. Le Manuel opératoire peut être demandé à tout moment auprès du fabricant. Le chirurgien établit une planification de l’opération qui fixe et consigne de façon appropriée les éléments suivants: •...
- Seite 50 Vis polyaxiale MACS • Les informations relatives à la technique opératoire, à l’as- sortiment d’implants et aux instruments d’implantation sont connues du chirurgien et de l’équipe chirurgicale; ces infor- mations sont disponibles sur place au complet • Le chirurgien et l’équipe opératoire sont au fait des règles de la pratique médicale, de l’état de la science et du contenu des parutions scientifiques correspondantes publiées par des auteurs médicaux...
- Seite 51 Vis polyaxiale MACS L’implantation du système MACS se fait selon les étapes sui- vantes: Choisissez la variante de système MACS appropriée et les vis d'ancrage en fonction de l'indication, de la planification préopératoire et de la situation osseuse constatée pendant l'opération.
- Seite 52 Vis polyaxiale MACS Retirez avec l’instrument de retrait approprié le fil Kirschner à travers l’instrument d’insertion à canule avant le déver- rouillage de ce dernier. Retirez l’instrument d’insertion. Vérifiez que les douilles de centrage demeurent temporaire- ment montées sur les éléments de serrage. Procédez éventuellement à...
- Seite 53 Vis polyaxiale MACS Implantez la plaque de stabilisation et les écrous de fixation de manière à ce que le côté portant l’inscription (face supérieure) soit visible pour l’exécutant. Danger de blessure si la stabilité de ser- rage des écrous est insuffisante! Placez les écrous correctement.
- Seite 54 Vis polyaxiale MACS Risque de blessure par fuites de ciment! Ne préparez et ne positionnez les implants qu’à l’aide de procédés d’imagerie. AVERTISSEMENT Contrôlez que les fentes de la vis po- lyaxiale XL sont entièrement dans l’os. Ne pénétrez pas dans le cortex op- posé...
- Seite 55 Vis polyaxiale MACS Mettez la vis de blocage en place. Risque de blessure par des vis de blocage impossibles à insérer ou à visser du fait du ciment en train de durcir! Insérez et vissez les vis de blocage AVERTISSEMENT immédiatement après avoir cimenté...
- Seite 56 Tornillo poliaxial MACS Finalidad de uso El tornillo poliaxial MACS XL se utiliza en combinación con el resto de implantes MACS del sistema MACS para la estabili- zación ventral de uno o varios segmentos de la columna vertebral lumbar y torácica. El sistema MACS se compone de: •...
- Seite 57 Tornillo poliaxial MACS Indicaciones Los implantes de uso quirúrgico refuerzan los procesos curativos normales. No deben reemplazar a las estructuras corporales nor- males ni, en caso de curación incompleta, soportar de forma du- radera las cargas existentes. Utilizar en caso de: •...
- Seite 58 Tornillo poliaxial MACS • Osteopenia aguda En caso de osteopenia, el cirujano deberá valorar los riesgos que podrían comprometer el éxito del tratamiento con el sis- tema MACS Si no se tienen garantías de que la estabilidad del tornillo po- liaxial estándar va a ser óptima, puede utilizarse el tornillo poliaxial XL.
- Seite 59 Tornillo poliaxial MACS Efectos secundarios e interacciones • Fallo del implante por sobrecarga – Doblamiento – Aflojamiento – Rotura • Fijación insuficiente • Sin fusión o fusión retardada • Fugas de cemento (escape de cemento de la vértebra) • Infección •...
- Seite 60 Tornillo poliaxial MACS • El cirujano deberá conocer a la perfección la anatomía del hueso, la posición de los nervios y los vasos sanguíneos, los músculos y los tendones. • El cirujano se responsabilizará de seleccionar todos los com- ponentes del implante y de implantarlos. •...
- Seite 61 Tornillo poliaxial MACS • Si se dañan las estructuras óseas que actúan como transmi- sores de fuerza, pueden producirse aflojamientos de los com- ponentes, fracturas óseas o de los implantes y otras compli- caciones graves. Para detectar cuanto antes causas de anomalías similares, tras la intervención debe comprobarse el estado del implante periódicamente mediante las medidas adecuadas.
- Seite 62 Tornillo poliaxial MACS Esterilización • Los componentes del implante se suministran sin esterilizar. • Los componentes del implante están envasados por separado. Conservar los componentes del implante en su envase origi- nal y no sacarlos del envase protector original hasta instan- tes antes de utilizarlos.
- Seite 63 Tornillo poliaxial MACS Aplicación El sistema MACS se describe en detalle en el manual quirúrgico. En la documentación del producto se incluyen instrucciones de utilización detalladas. El manual quirúrgico puede solicitarse al fabricante en cualquier momento. El cirujano realizará una planificación quirúrgica en la que se es- tablecerá...
- Seite 64 Tornillo poliaxial MACS • Instrumental especial preparado para la implantación de los elementos, la distracción, compresión y reposición de la co- lumna vertebral lumbar y torácica • Tanto el cirujano como el equipo de quirófano tienen la in- formación necesaria sobre la técnica operatoria, los implan- tes y el instrumental;...
- Seite 65 Tornillo poliaxial MACS La implantación del sistema MACS requiere los siguientes pa- sos: Seleccionar la variante del sistema MACS y los tornillos de anclaje adecuados en función de la indicación, la planifica- ción preoperatoria y la situación ósea disponible intraopera- toriamente.
- Seite 66 Tornillo poliaxial MACS Retirar el instrumento de inserción. Asegurarse de que los casquillos de centraje permanecen montados temporalmente sobre los elementos de sujeción. En caso necesario, distraer y colocar un mantenedor de espa- cio. Peligro de lesiones por aflojamiento o arranque de los tornillos durante la repo- sición, la distracción o la compresión, en especial en casos de mala calidad ósea.
- Seite 67 Tornillo poliaxial MACS Implantar la placa estabilizadora y las tuercas de fijación de for- ma que la cara grabada (cara superior) quede a la vista del usua- rio. Peligro de lesiones si las tuercas no quedan sujetas suficientemente. Colocar correctamente las tuercas. Apretar las tuercas con una llave dina- ADVERTENCIA mométrica a 15 Nm.
- Seite 68 Tornillo poliaxial MACS Peligro de lesiones por fugas de cemento. La preparación y colocación de los implantes debe realizarse únicamente con la ayuda de procedimientos de ADVERTENCIA creación de imagen. Asegurarse de que las ranuras del tor- nillo poliaxial XL se han introducido por completo en el hueso.
- Seite 69 Tornillo poliaxial MACS Colocar el tornillo aprisionador. Peligro de lesiones por la imposibilidad de colocar o apretar los tornillos aprisionado- res debido al fraguado del cemento. Colocar y apretar los tornillos aprisio- ADVERTENCIA nadores inmediatamente después de cementar el tornillo poliaxial XL. Peligro de lesiones si los tornillos aprisio- nadores no están lo suficientemente intro- ducidos en los elementos poliaxiales.
- Seite 70 Vite poliassiale MACS Destinazione d’uso La vite poliassiale MACS XL è concepita per eseguire, in combi- nazione con gli altri impianti MACS del sistema MACS , stabi- lizzazioni ventrali monosegmentali e multisegmentali del tratto lombare e toracico del rachide. Il sistema MACS è...
- Seite 71 Vite poliassiale MACS Indicazioni Gli impianti applicati chirurgicamente servono a supportare i normali processi di guarigione. Non sono destinati né a sostituire le normali strutture corporee, né ad assorbire in maniera perma- nente le sollecitazioni presenti nei casi di ritardata guarigione. Utilizzabili per: •...
- Seite 72 Vite poliassiale MACS • Osteopenia grave Nei casi di osteopenia l’operatore deve ponderare i rischi che potrebbero compromettere la riuscita della terapia con il si- stema MACS In caso di prevista minor tenuta della vite poliassiale standard è possibile utilizzare la vite poliassiale XL. Per aumentare ul- teriormente la stabilità...
- Seite 73 Vite poliassiale MACS Effetti collaterali ed interazioni • Fallimento dell’impianto dovuto ad eccessive sollecitazioni – deformazione – allentamento – rottura • Fissaggio insufficiente • Mancata o ritardata fusione • Perdite di cemento (fuoriuscita di cemento dal corpo vertebrale) • Infezioni •...
- Seite 74 Vite poliassiale MACS • L’operatore deve conoscere perfettamente l’anatomia ossea, compreso l’andamento di nervi, vasi sanguigni, muscoli e tendini. • L’operatore è responsabile del corretto abbinamento dei componenti e del relativo impianto. • Aesculap non risponde di eventuali complicanze dovute ad errata identificazione delle indicazioni, scelta di componenti dell’impianto non idonei e tecnica operatoria non corretta, nonché...
- Seite 75 Vite poliassiale MACS • In caso di danni delle strutture ossee preposte alla trasmis- sione delle forze non si possono escludere allentamenti dei componenti, fratture ossee o dell’impianto ed altre compli- canze gravi. Per identificare con la massima tempestività possibile tali fonti di problemi, dopo l’intervento chirurgico è...
- Seite 76 Vite poliassiale MACS Sterilità • Al momento della consegna i componenti dell’impianto non sono sterili. • I componenti dell’impianto sono imballati in una confezione singola. Conservare i componenti dell’impianto nella confezione ori- ginale ed estrarli dall’imballo protettivo originale solo imme- diatamente prima dell’uso.
- Seite 77 Vite poliassiale MACS Impiego Il sistema MACS è dettagliatamente illustrato nel relativo ma- nuale dell’intervento. Istruzioni per l’uso dettagliate sono ripor- tate nella documentazione relativa al prodotto. Il manuale dell’intervento può essere richiesto al produttore in qualsiasi momento. L’operatore deve effettuare una pianificazione dell’intervento che definisca e documenti in maniera idonea i seguenti punti: •...
- Seite 78 Vite poliassiale MACS • L’operatore e l’équipe operatoria devono conoscere le infor- mazioni relative alla tecnica operatoria, l’assortimento di im- pianti e lo strumentario; tali informazioni devono inoltre es- sere interamente disponibili in loco • Devono essere note e rispettate le regole della scienza medi- ca, lo stato dell'arte della stessa, nonché...
- Seite 79 Vite poliassiale MACS L’impianto del sistema MACS prevede le seguenti fasi operato- rie: Scegliere la variante del sistema MACS e le viti di ancorag- gio idonee in conformità all’indicazione, alla pianificazione preoperatoria ed alla situazione ossea accertata durante l’in- tervento. Determinare la posizione ottimale per l’impianto del sistema MACS –...
- Seite 80 Vite poliassiale MACS Prima di sbloccare lo strumento inseritore, estrarre il filo di Kirschner attraverso lo strumento inseritore cannulato con l’apposito estrattore. Rimuovere lo strumento inseritore. Accertarsi che le boccole di centraggio rimangano tempora- neamente montate sugli elementi di serraggio. Eventualmente distrarre ed inserire un segnaposto.
- Seite 81 Vite poliassiale MACS Impiantare la placca di stabilizzazione ed i dadi di fissaggio in modo che il lato con l’iscrizione (lato superiore) rimanga visibile per l’utente. Pericolo di lesioni dovute ad una stabilità di serraggio insufficiente dei dadi! Applicare correttamente i dadi. Stringere i dadi a 15 Nm con una chiave AVVERTENZA torsiometrica.
- Seite 82 Vite poliassiale MACS Pericolo di lesioni dovute a perdite di ce- mento! Preparare e posizionare gli impianti solo con l’ausilio di procedimenti di diagno- AVVERTENZA stica per immagini. Accertarsi che gli intagli della vite po- liassiale XL siano posti completamente nell’osso.
- Seite 83 Vite poliassiale MACS Inserire la vite di arresto. Pericolo di lesioni dovute a viti di arresto che non possono essere utilizzate o strette a causa del cemento in fase di indurimento! Applicare e stringere le viti di arresto AVVERTENZA subito dopo la cementazione della vite poliassiale XL.
- Seite 84 Parafuso poliaxial MACS Aplicações O parafuso poliaxial MACS XL é usado em combinação com ou- tros implantes MACS pertencentes ao sistema MACS , que se destina à estabilização ventral mono e multi-segmental da colu- na vertebral torácica e lombar. O sistema MACS é...
- Seite 85 Parafuso poliaxial MACS Indicações Os implantes colocados por via cirúrgica destinam-se a ajudar os processos normais de recuperação. Eles não se destinam a substituir estruturas normais do corpo nem, no caso de falta de recuperação, a suportar duradouramente os esforços que incidem sobre a parte afectada do corpo.
- Seite 86 Parafuso poliaxial MACS • Osteopenia grave No caso de osteopenia, o cirurgião deve ponderar os benefí- cios e os riscos que podem de pôr em risco um tratamento bem sucedido com o sistema MACS No caso de suspeita de má fixação do parafuso poliaxial stan- dard, pode usar-se o parafuso poliaxial XL.
- Seite 87 Parafuso poliaxial MACS Efeitos secundários e interacções • Deficiência do implante por esforço excessivo – Flexão – Relaxamento – Quebra • Fixação insuficiente • Falta de fusão ou fusão tardia • Fugas de cimento (cimento derrama para fora do corpo vertebral) •...
- Seite 88 Parafuso poliaxial MACS • O cirurgião deverá dominar, tanto na teoria como na prática, as técnicas reconhecidas de operação. • O cirurgião tem de estar absolutamente familiarizado com a anatomia dos ossos, com o percurso dos nervos e dos vasos sanguíneos, assim como dos músculos e dos tendões.
- Seite 89 Parafuso poliaxial MACS • No caso de lesão das estruturas ósseas que suportem o peso do corpo não se exclui a incidência de possíveis relaxamentos dos componentes, fracturas do osso ou do implante e outras complicações graves. Para se detectar, com a maior precocidade possível, estas causas de complicações, é...
- Seite 90 Parafuso poliaxial MACS Esterilidade • Os componentes do implante são fornecidos em condições não esterilizadas. • Os componentes do implante são embalados separadamente. Guardar os componentes do implante na embalagem original e tirá-los da embalagem original ou da embalagem protecto- ra apenas no momento da sua utilização.
- Seite 91 Parafuso poliaxial MACS Utilização O sistema MACS está descrito de forma pormenorizada no ma- nual cirúrgico. Para instruções de utilização pormenorizadas, queira consultar a documentação sobre o produto. O manual cirúrgico pode ser encomendo a qualquer momento no fabricante. O cirurgião elaborará um plano da operação, o qual determinará e documentará...
- Seite 92 Parafuso poliaxial MACS • Os instrumentos especiais necessários para a implantação dos elementos, assim como para a distracção, a compressão e a reposição da coluna vertebral lombar e torácica, foram devidamente preparados • O cirurgião e a equipa operatória conhecem as informações necessárias à...
- Seite 93 Parafuso poliaxial MACS A implantação do sistema MACS requer os seguintes procedi- mentos: Escolher a variante adequada do sistema MACS , bem como os parafusos de fixação com base na indicação, no plano pré- operatório e nas condições ósseas que se apresentam duran- te a intervenção.
- Seite 94 Parafuso poliaxial MACS Não apertar nem introduzir completamente o parafuso poli- axial XL, de forma a permitir um movimento do elemento tensor. Antes de destravar o instrumento introdutor, remover o fio de Kirschner através do instrumento introdutor canulado, usan- do o instrumento extractor adequado. Remover o instrumento introdutor.
- Seite 95 Parafuso poliaxial MACS Implantar a placa de estabilização e as porcas de fixação de for- ma a que o lado com a gravação (lado de cima) fique virado para o utilizador. Perigo de ferimento no caso de estabilidade insuficiente de aperto da porca! Colocar as porcas correctamente.
- Seite 96 Parafuso poliaxial MACS Perigo de ferimento devido a fugas de ci- mento! Preparar e posicionar os implantes ape- nas com a ajuda de técnicas imageológi- AVISO cas. Assegurar que as ranhuras do parafuso poliaxial XL ficam completamente imer- gidas no osso. Não penetrar a contracortical óssea e assegurar-se que a contracortical não foi lesada (por ex.
- Seite 97 Parafuso poliaxial MACS Inserir o parafuso de aperto. Perigo de ferimento devido a cimento endu- recido que impossibilita a introdução e o aperto do parafuso de aperto! Inserir e apertar o parafuso de aperto AVISO logo a seguir à cimentação do parafuso poliaxial XL.
- Seite 98 MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL Gebruiksdoel De MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL dient in combinatie met de an- dere MACS -implantaten van het MACS -systeem voor de ven- trale mono- en multisegmentale stabilisatie van de lumbale en thoracale wervelkolom. Het MACS -systeem bestaat uit: •...
- Seite 99 MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL Indicaties Operatief ingebrachte implantaten dienen ter ondersteuning van het normale genezingsproces. Ze zijn niet bedoeld om normale li- chaamsstructuren te vervangen, noch om langdurig optredende belastingen te dragen in geval van onvolledige genezing. Te gebruiken bij: •...
- Seite 100 MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL • Ernstige osteopenie Bij osteopenie moet de operateur de risico's afwegen die het succes van de behandeling met het MACS -systeem in het gedrang kunnen brengen. In geval van te verwachten beperkte houvast van de stan- daard polyaxiale schroef kan de polyaxiale schroef XL worden gebruikt.
- Seite 101 MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL Neven- en wisselwerkingen • Beschadiging van het implantaat door overbelasting – Buiging – Loskomen – Breuk • Slechte fixatie • Geen of vertraagde fusie • Cementlekkage (cementuitloop buiten het wervellichaam) • Infectie • Fractuur van het wervellichaam •...
- Seite 102 MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL • De operateur moet absoluut vertrouwd zijn met de botana- tomie, het verloop van de zenuwen en bloedvaten, de spieren en pezen. • De operateur is verantwoordelijk voor de samenstelling van de implantaatcomponenten en hun implantatie. •...
- Seite 103 MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL • Bij beschadiging van de krachtoverbrengende botstructuren kunnen het loskomen van componenten, bot- en implantaat- fracturen en andere ernstige complicaties niet uitgesloten worden. Om dergelijke problemen zo vroeg mogelijk op te sporen, moet de toestand van het implantaat na de operatie regel- matig met gepaste technieken worden gecontroleerd.
- Seite 104 MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL Steriliteit • De implantaatcomponenten worden onsteriel geleverd. • De implantaatcomponenten zijn afzonderlijk verpakt. Bewaar de implantaatcomponenten in de originele verpak- king en haal ze pas net voor gebruik uit hun originele en be- schermende verpakking. Reinig de implantaten voor gebruik en steriliseer ze met stoom (volgens de sterilisatievoorschriften van het betref- fende ziekenhuis).
- Seite 105 MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL Toepassing Het MACS -systeem wordt uitvoerig beschreven in de OP-ma- nual. Gedetailleerde gebruiksinstructies vindt u in de productdo- cumentatie. De OP-manual kan altijd bij de fabrikant worden besteld. De operateur stelt een operatieplanning op, waarin het volgende vastgelegd en degelijk gedocumenteerd wordt: •...
- Seite 106 MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL • De regels van de medische kunst, de huidige stand van de wetenschap en de inhoud van wetenschappelijke publicaties van de medische auteurs zijn bekend • Inlichtingen ingewonnen bij de fabrikant in geval van een onduidelijke preoperatieve situatie en bij implantaten in het te behandelen deel van de wervelkolom De patiënt werd over de ingreep geïnformeerd en heeft zich schriftelijk akkoord verklaard met de volgende informatie:...
- Seite 107 MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL Bepaal de optimale implantaatpositie voor het MACS -sys- teem: – Positioneer het implantaat voorlopig met Kirschner-dra- den en – bereid het bot zorgvuldig voor met gecanuleerde instru- menten. Gebruik de implantatie-instrumenten correct. Om interne spanningen te vermijden en de implantaten niet te verzwakken: Groeven en krassen in alle componenten vermijden.
- Seite 108 MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL Distraheer eventueel en breng plaatshouders aan. Gevaar voor verwonding door loskomen of lostrekken van de schroeven tijdens de repositie, distractie of compressie, vooral bij een slechte botkwaliteit! WAARSCHUWING Wend voorzichtig en gedoseerd kracht aan. Zorg voor een permanente visuele controle (direct of met behulp van beeldvormingstechnieken).
- Seite 109 MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL Volg de veiligheidsinstructies voor het Aesculap-cement- applicatiesysteem altijd. Gevaar voor verwonding door cement- lekkage! Prepareer en positioneer de im- plantaten altijd met behulp van WAARSCHUWING beeldvormingstechnieken. Let erop dat de gleuven van de po- lyaxiale schroef XL volledig in het bot zitten.
- Seite 110 MACS -polyaxiale schroef XL Breng de klemschroef aan. Gevaar voor verwonding door niet-be- vestigbare of aanspanbare klemschroe- ven ten gevolge van uithardende cement! WAARSCHUWING Breng de klemschroeven onmiddel- lijk na het cementeren van de polyaxiale schroef XL aan en span ze meteen aan.
- Seite 112 CE-Kennzeichnung gemäß Richtlinie 93/42/EWG CE marking according to directive 93/42/EEC Marquage CE conforme à la directive 93/42/CEE Identificación CE en conformidad con la directriz 93/42/CEE Marchio CE conforme alla direttiva 93/42/CEE Simbolo CE, em conformeidade com a Directiva 93/42/CEE CE-certificering conform richtlijn 93/42/EEG Technische Änderungen vorbehalten Technical alterations reserved Sous réserve de modifications techniques...






